Constitutional Law
Constitutional Law- Law Notes, Judiciary, Notes Case Law, Judgments Historical overview and nature of the Indian Constitution, Union and its Territory, Concept of ‘State’ under Article 12, Article 13 and Power of Amendment under Article 368. Case Analysis: Indra Sawhney v. Union of India (1993) Fundamental Rights and Directive Principles of State Policy, Anti-Defection Law / Tenth Schedule.
Important Amendments to Indian Constitution to (105th)
Important Amendments to Indian Constitution (105th) Amendments in Indian Constitution are necessary to satisfy the demands of the time. The power to amend the ...
Cases of Article 21 Indian Constitution with Short explanation
Cases of Article 21 Indian Constitution with Short explanation Cases of Article 21 Indian Constitution Article 21 reads as: “No person shall be ...
Difference between Indian Constitution and American Constitution
Difference between Indian Constitution and American Constitution Difference between Indian Constitution and American Constitution Indian Constitution 1. Indian federation is not the result of ...
Difference between Indian Constitution and American Constitution
Difference between Indian Constitution and American Constitution Indian Constitution 1. ...
Difference Between Money Bill and Finance Bill: Our Legal World
Difference Between Money Bill and Finance Bill Money Bill Only those financial bills which contain provisions exclusively on matters listed in article 110 of the ...
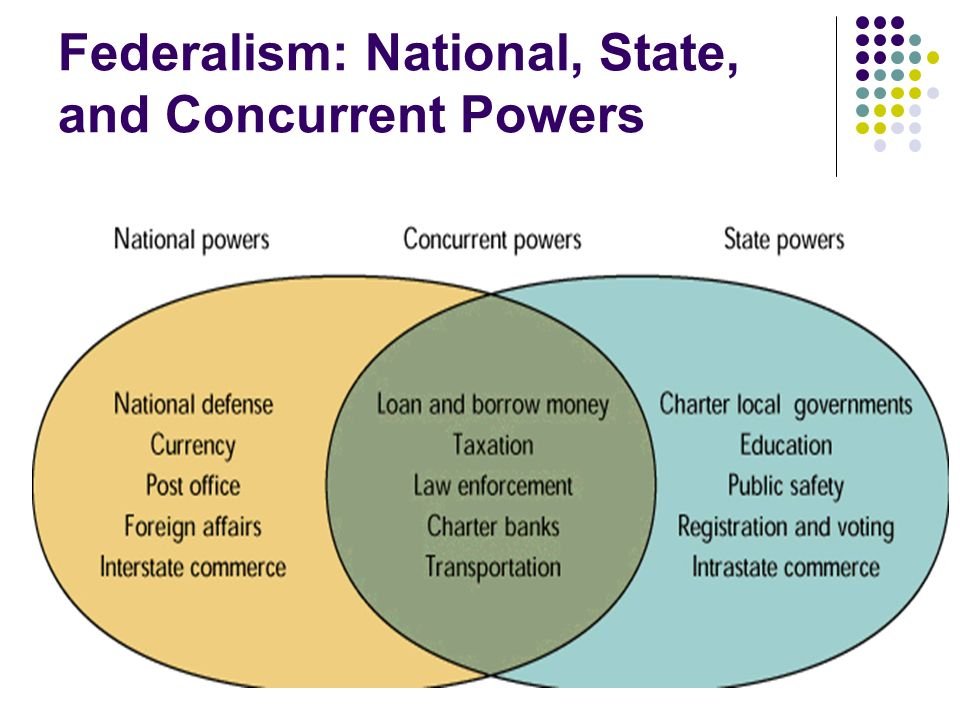
Overview of Indian Federalism and its Judicial Approach
Overview of Indian Federalism and its Judicial Approach ...
Privilege against self-Incrimination in INDIA
Privilege against self-Incrimination in INDIA Fundamental Right is the essential human rights of all citizens or person. Fundamental Rights history started from many documents ...
Can a person waive any of the Fundamental Rights?
Can a person waive any of the Fundamental Rights? Fundamental Rights are a basic rights or Natural Right of the people and the charter ...
Privilege against self-Incrimination and Article 20(3) in INDIA
Privilege against self-Incrimination and Article 20(3) in INDIA Fundamental Right is the essential human rights of all citizens or person. Fundamental Right history started ...